
“EARTH RISING”
The very first photo humans saw of our common home from our closest orbiting planet.
This NASA created shot was impressed upon billions of minds at the time Apollo 8 is said to have taken this photo
And reinforced hundreds, if not millions of times in global media.
Van Gough, Rembrant, et al. would be ashamed of such amateurish work.
Still, billions believed and still believe to this day, that this is a real photograph.
*****
What do you really see above in the most famous picture in the World?
Suspend belief for a few moments in your life. What do you just see in the above picture?
Look at the “blue marble” as it is called. Incredible detail of the Earth, it’s clouds and even patches of green and brown. A perfect globe with such detail though the deep blue see is what covers our skies looking up this way. Why doesn’t the ocean blue overwhelm the photo from space void of atmosphere, like we see the other planets?
The Moon’s horizon is level and flat right to left, yet due to the Moon being 1/4 the Earth, curvature should be seen easily?
And where are those dang billions and billions of stars we see in space from Earth at night?
The Moon is so reflective that it lights up or Earth at night so bright we can see easily during a full moon, yet Moon’s surface is a dull, dusty least reflecting color, gray.

One other thing to keep in mind. Due to no atmosphere the temperatures range each day on the sunny side ranged from a – 387 F degrees to a plus 225 F. Yet all cameras worked great. The film worked great. The Land Rover, no problems, the radio and tv worked awesome. The space suits, just millimeters thick and so flexible they creased, keep cooled, no worries mate, depsite having to carry gallons and gallons of water in their packs to run their inner A/C.
*****
“One Giant Blunder for Mankind, how NASA lost the moon pictures”,
… read the world news headlines in 2006. Just at the time digital imaging was taking apart the NASA photos, they went lost. (Source)
The missing tapes were among over 700 boxes of magnetic data tapes recorded throughout the Apollo program which have not been found.[14] On August 16, 2006 NASA announced its official search saying, “The original tapes may be at the Goddard Space Flight Center … or at another location within the NASA archiving system“, “NASA engineers are hopeful that when the tapes are found they can use today’s digital technology to provide a version of the moonwalk that is much better quality than what we have today.“
At the bottom of this post are the debunker’s replies to many of the pictures many questions aksed. It is whole other effort to read the reason the pictures are lying to our eyes from those that know we went to the moon.
(as you scroll down to the next picture, see how many flaws you can point out and then see how it matches against the pro CGI specialists)
***
“You gonna believe me or your lying eyes?”
Every single one of these pictures as well as all pictures of space travel, have come from NASA alone.
 |
BornWernher Magnus Maximilian, Freiherr von Braun
March 23, 1912
Wirsitz, Posen Province, Prussia, German Empire
(modern Wyrzysk, Piła County, Poland)
Wernher Magnus Maximilian, Freiherr von Braun (March 23, 1912 – June 16, 1977) was a German and later American aerospace engineer and space architect. He was one of the leading figures in the development of rocket technology in Germany and the United States and is considered one of the “Fathers of Rocket Science“. He was also a member of the Nazi party and the SS, and was suspected of perpetrating war crimes during World War II.
NASA was founded in 1958 by the Department of Defense.
In the late 1940’s through the 1960’s, the United States government brought known Nazi German scientists into the country illegally and quietly through Operations Paperclip (Source). Even the Presidents did not know about this operation until the 1960’s.
Some 3200 scientists were brought over in all an installed in U.S. military and corporate hierarchy. The Vatican provided the passport by establishing “ratlines” as the Nazi’s first journeyed to Argentina and then up to the United States. (Source)
Nazi Werhner Von Bruan was the “wunderkind” rocket builder who designed, built and then launched the deadly V1 and V2 “buzz bombs” that killed tens of thousands of allies in European during WWII.
He was then brought over to the U.S where he started when NASA was founded and ran NASA’s Saturn rocket program for 26 years straight. (Source).
NASA has released nearly ten thousand pictures from space. (source) Most of the pictures from space exploration and moon landings were released after 1991.
EVERY SINGLE PICTURE OF THE COSMOS COMES FROM NASA CONTROLLED ENTITIES.
****
Matthew Boylan, former NASA operational graphics manager, worked for years creating photo-realistic computer graphics for NASA. Now a vocal Flat-Earther, Boylan claims that NASA’s sole reason for existence is to propagandize the public and promote this false ball-Earth heliocentric worldview. Originally recruited because of his skills and reputation as a hyper-realist multi-media artist, he started doing projects like photoshopping various lighting and atmospheric effects onto images of Earth, the Moon, Jupiter, Europa, etc. Having proved himself, and wanting to promote him to do more classified work, a room of NASA higher-ups during a party, as a type of initiatory-rite, explained to him and a few others in detail the reality of the Geocentric Flat-Earth model and how they have fooled the entire world!
Refusing to be a part of their deception, Boylan cut his ties to NASA, began researching the Flat-Earth for himself, and has recently become a powerful voice on the lecture circuit and the internet exposing NASA and their heliocentric hoax. In his comedic lectures he speaks candidly and eloquently about how simple it is using nothing more than Adobe Photoshop and a video editor to create any and every type of image NASA purports to be “receiving from the Hubble telescope.” He points out how in most ball-Earth videos lazy NASA graphics workers don’t even bother changing cloud structures in ordinary or time-lapse footage; the same shape, color and condition cloud cover often stays completely unchanged for 24 hour periods and longer! Boylan states unequivocally that every picture and video of the ball-Earth, all the Moon/Mars landings, the existence of orbiting satellites, space stations, and all Hubble images are hoaxed. He even quips anecdotes about how NASA officials and astro-nots privy to the Flat-Earth truth would laugh hysterically at the brain-washed zombie public who unquestioningly believe their televisions.
****
REMEMBER, IF ONE PICTURE IS PHOTOSHOPPED, THEY ARE ALL TO BE ASSUMED FALSE AS WELL
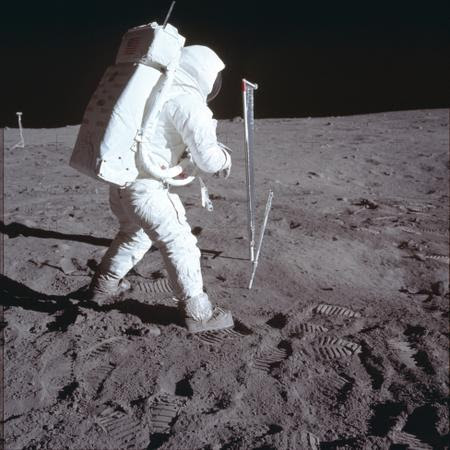
“ONE MALL STEP FOR MAN; ONE GIANT LEAP FOR MANKIND”
Said to be the first footprint on the Moon by Neil Armstrong.

Note the lack of impression, or depression. The heel and outside shadows prove the boot is higher than the surface. The Moon’s surface has little atmosphere with no water so how does the shape even occur? ( Think of being on a beach, with water one gets a footprint but absent of water, just a rough outline.)

Here we have impressions. If an astronot weighing 1/6th the weight on Earth can make that kind of impression, what kind of impression would a lunar landing module onto the surface? (answer later)
****

This is one of the most famous of all Moon astronot pictures. Apollo missions had three onboard. One stayed with the command module while two others allegedly went to the Moon surface. Look in the helmet reflection.
1) If the Sun was so strong, and coming from his left, the visors curve side towards the Sun would be glared.
2) The shading should be much darker on the right side of his suit. Look how bright the light is.
3) Yes, THREE, not two astronots in this photo. One, the photographer, two the guy in the visor background and three, astronot Buzz Aldrin.
4) No stars in the background, yet no light pollution like on Earth to obfuscate the stars.
****

This picture is the best though! Look in HIS helmet and if you didn’t see two astronauts on the last photo, you will now. There’s the 2 men you see in the helmet + the one being photographed. That = 3 men on the moon at once. Remember there were only 2 at a time. Also notice that in the previous photo, the 2nd astronaut has been taken out. Yes they are identical photos.
*****

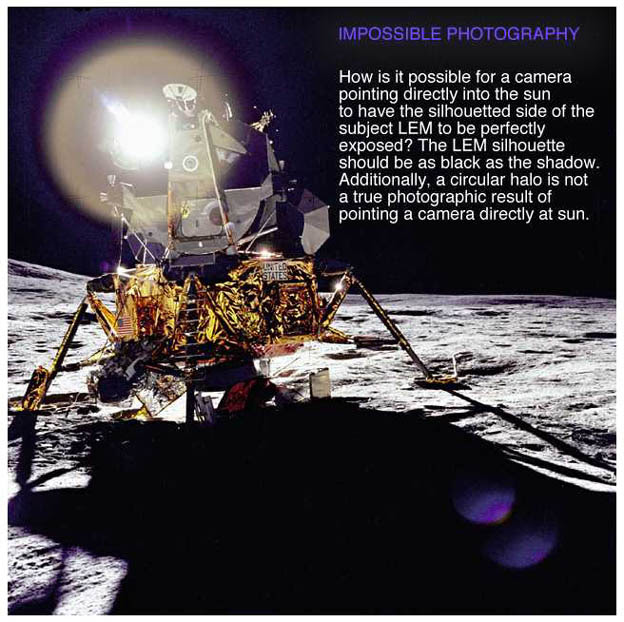
This next picture is also a well know photograph called “Man on the Moon”. This picture is very mind boggling to me. In area (B), there is a shadow being cast over the astronauts space suit. Again, if the sun is the only light source and if there is no atmosphere on the moon, the shadow should be MUCH darker.
In the background labeled (C), you can plainly see that the farther back you look it fades darker and darker until finally it’s black. This happens on the Earth due to our atmospheric geography, but the moon has no atmosphere which means the horizon should not be faded but should be very sharp, distinct and crystal clear. Letter (D) shows something floating just above the moon’s surface
****

(Steven wasn’t the best of class early on but got a lot better at editing and CGI later in his career.)
*****
The official story told/sold in real time to billions in absolute awe and amazement in 1969.
First Moon Landing 1969
The video of the very first moon landing of the apollo 11 mission on July 21, 1969! Neil Armstrong was the first man to set foot on the moon with his now legenday words “One small step for man, a giant leap for mankind.”
The video feeds all came from three NASA owned satellites and beamed into the NASA control room in Houston. All TV stations were required to use the one NASA feed which increased the grainy, fuzzy picture. It was broadcast live and fed around the world. The world was in complete awe and amazement.
” While still on the steps, Armstrong deployed the Modularized Equipment Stowage Assembly from the side of the Lunar Module. This housed, amongst other things, the TV camera. This meant that upward of 600 million people on Earth could watch the live feed.”
Who Shot the Picture?
This picture is from Wiki. It is included as the first step on the moon in his bio. Note the the Sun locations versus the above video. Completely different. Where are any stars? Look how dark the machines shadows are, but Mr. Armstrong is defined.
Who took the picture? NASA says they had a swing arm from the LEM, that’s some long arm.
Did they send and advance photo shoot team to ready for the historic, never happened before photo op? Pretty cool also that sun was just low enough, to make such dark shadows, except for Mr. Armstrong. And the slope of that Moon! Did he fall backwards and fall down on his first step? Now that would be a conspiracy, wouldn’t it?
****

The previous picture is of Armstrong touching the Moon taken from the alleged swing arm camera he lowered down to take the famous shot. How come we can’t see the camera in any pictures such as this? This was taken by Armstrong and shows Buzz Aldrin climbing out and getting ready to climb down the ladder. Where’s the camera that just a minute or two prior, videoed Neil making his decent?
****
On the return trip home, gazing through 240,000 miles of space toward the stars and the planet from which I had come, I suddenly experienced the universe as intelligent, loving, harmonious.”
― Edgar D. Mitchell Commander Apollo 14

Again the dark, dark shadows cast but light on the legs and the astronot is clearly visible as well as the American flag which should be black like the shadows. There were no ambient lights brought on the missions.
****

A photographer simply added light to the NASA photo and got strange background images.
***
“A galaxy is composed of gas and dust and stars—billions upon billions of stars.” Carl Sagan

One of the most famous pictures ingrained in all minds of the world. Buzz Aldrin saluting the U.S. flag as U.S. claims the Moon for its own…is the official narrative.
Note: No stars. Flat landscape. Flag is waving but there isn’t wind of the Moon, NASA says. Look at the Flag and the shadow of the pole it DOESN’T make. Sun is coming low (long shadows) and directly at the flag yet no shadow. Also not how the background is always very poorly defined in NASA pictures.
“Houston, it’s been a real change for us. Now we are able to see the stars again and recognize constellations for the first time on the trip. The sky is filled with stars, just like the nights out in Earth” 1st Man on the Moon, ~ Neil Armstrong

With Flag Shadow now. Firm flag. Background dull and flat. U.S. flag can easily be seen on the dark side of the LEM. No stars.

The black sky should be full of stars, yet none are visible in any of the Apollo photographs.
This claim is one I hear frequently, and is one of the easiest to refute. The answer is very simple: they are too faint. The Apollo photos are of brightly lit objects on the surface of the Moon, for which fast exposure settings were required. The fast exposures simply did not allow enough starlight into the camera to record an image on the film. For the same reason, images of Earth taken from orbit also lack stars. The stars are there; they just don’t appear in the pictures. The hoax advocates often argue that stars should be visible, and some of their claims are valid, however they fail to recognize the difference between “seeing” stars and “photographing” stars. The astronauts could have recorded star images in their photos by increasing exposures, but they were not there to take star pictures. The purpose of the photos was to record the astronauts’ activities on the surface of the Moon.
Bill Kaysing claims that NASA has perpetrated the lie that stars cannot be seen in space to validate the lack of stars in the Apollo photos. This assertion is utterly ridiculous; in fact, NASA has released many photos in which stars are visible. Common among these are long-exposure nighttime photographs of aurora taken by space shuttle astronauts. This example [see photo] is a four-second exposure taken from the flight deck of the shuttle Endeavour.
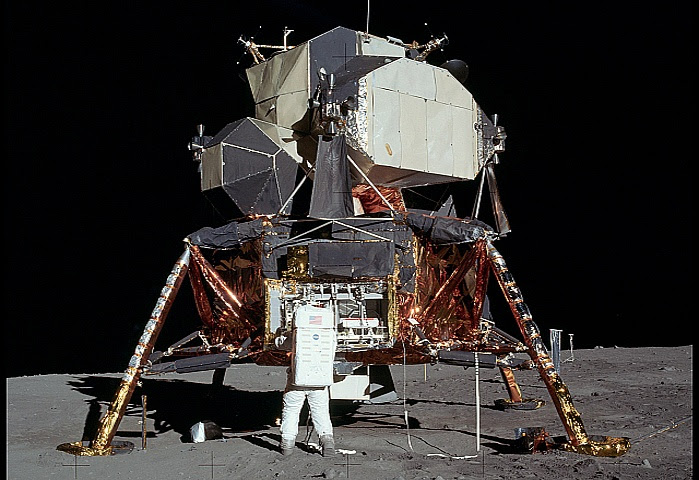

This looks almost surreal. Again NO Stars, no dust particles, no crater or any type of impressions from the impact of the landing. Note the huge engine nozzle behind the astronot. Also look at the shape of the LMT upper module. How the heck does that thing even fly. It is a box with many obtuse angles, yet it was steered back into space and docked with the command module?
***
…Starry, starry night…depends on which astronot your ask?
****

Water for cooling the cabin, oxygen for air and fuel to launch back into space all had to be included in the tiny lower base that stayed on the moon.
The No Ignition, No Dust Rapid LEM Takeoff from Moon
First, how did this thing fly???. There is no external output of energy. No flame, no blast from the exhaust nozzle. Look again at the above picture of how friggin’ big that thing was. Yet no visual from official sources. And never, ever a glimmer of a star in the blackness of outer space with no light pollution.
****

What about now? See any stars? No Moon reflection up here in black, dark space, right?
NASA had to omit all stars from their faux photos because amateur astronomers would be able to pick apart and wrong, or inaccurate, star formation. No stars, no problemo!

This one of NASA’s most famous pictures allegedly taken from the capsule of Apollo 12 as the LMT come up from the Moon to dock with the Command Module. Again, no stars. Again, how the heck does physics allow this completely non-aerodynamic craft to go through, much less maneuver so fragily as to dock up with another orbiting craft?
Note also that the Earth is so in focus that even the details of the clouds, only a few thousand miles above Earth, are clearly outlined.
****

The cameras used by astronauts during the moon landings had a multitude of cross-hairs to aid with scaling and direction. These are imprinted over the top of all photographs. Some of the images, however, clearly show the cross-hairs behind objects in the scene, implying that photographs may have been edited or doctored after being taken. The photograph shown above is not an isolated occurrence. Many objects are shown to be in front of the cross-hairs, including the American flag in one picture and the lunar rover in another.
****
“Outside my window I can see stars – and that is all. Where I know the moon to be, there is simply a black void; the moon’s presence is defined solely by the absence of stars”. Michael Collins, coming around from the Dark Side of the Moon.

Stage light reflection. No stars. No impression from jet engine exhaust while landing. This machine had to have enough power to slow the module to almost a standstill for landing, yet no impressions?
*****
When you see pictures of astronots in zero gravity, even small globs are floating around in near weightlessness gravity
Yet no moon dust is kicked up at all?
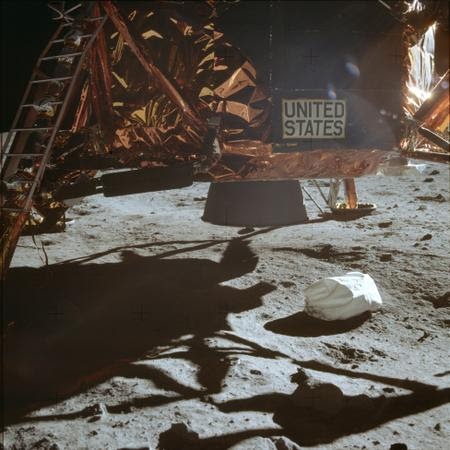


“Vostok II plunged with a rush into the inky blackness of the planet’s shadow, and as my eyes quickly adapted to the change I stared in wonder at the huge stars that glittered like diamonds”. ~ Ghermin Titov, Cosmonot who orbited Earth 17 times.
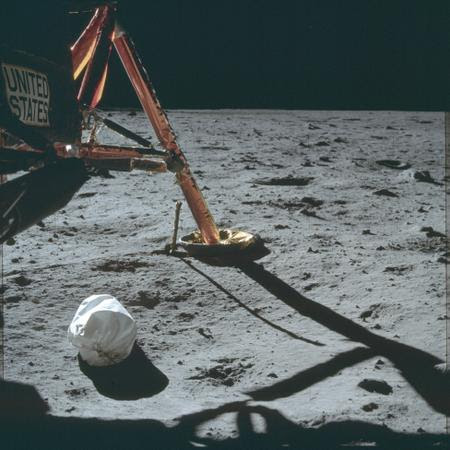

Again, no crater. U.S. name in complete shadow, look at angle of sun from shadow, but name is very visible. Also note, no curvature of the Moon which is 1/4 the size of Earth or 1080 miles across. This would be easily visible on any horizon Moon shots. It’s a globe, it has round “edges”.
Yet footprints galor made from Man

****
(Note same photo as in first few pics, yet author here cannot count the number of astronots needed to make this shot truthful.)

After photographs of the moon landings were released, theorists were quick to notice a mysterious object (shown above) in the reflection of an astronaut’s helmet from the Apollo 12 mission. The object appears to be hanging from a rope or wire and has no reason to be there at all, leading some to suggest it is an overhead spotlight typically found in film studios.
The resemblance is questionable, given the poor quality of the photograph, but the mystery remains as to why something is being suspended in mid-air (or rather lack of air) on the moon. The lunar module in other photos appears to have no extension from it that matches the photo, so the object still remains totally unexplained.
****

Note small pole. NO shadow. No stars.
****

On the moon there is only one strong light source: the Sun. So it’s fair to suggest that all shadows should run parallel to one another. But this was not the case during the moon landing: videos and photographs clearly show that shadows fall in different directions.
****
 ‘
‘
****
All Photos presented are from Official NASA sources


The Moonbuggy leaves depressions even though the Moon has not moisture to create impressions.


No stars. You can also see the line where the foreground and flat background where seemed. Maybe DARPA’s photoshopping wasn’t that as developed. Yet there must of been great pressure on these guys to get out the thousands and thousands of photos said to have been taken. Another mystery is how the astronots had the time to take so thousands of photos when most moon walks were under and hour.

Moon buggies were used on Apollo 15-17. Impossible for any vehicle to make a straight right angle turn. Also look at shadows on measurement device and rocks. They clearly are going in different directions.
*****

How did this machine get there?, depth focus dissapates too quickly. look at extendo sampler arm..
no stars. no moon buggy or tracks.
****

****

The two photos from the Apollo 15 mission shown above clearly have identical backdrops, despite being officially listed by NASA as having been taken miles apart. One photo even shows the lunar module. When all photographs were taken the module had already landed, so how can it possibly be there for one photo and disappear in another? Well, if you’re a hardcore conspiracy theorist, it may seem viable that NASA simply used the same backdrop when filming different scenes of their moon landing videos.
NASA has suggested that since the moon is much smaller than Earth, horizons can appear significantly closer to the human eye. Despite this, to say that the two hills visible in the photographs are miles apart is incontrovertibly false.
****

Whole lot of instruments to be working so well in so much hear and sun intensity.

(Just think how long it would take to unpack and assemble this in 150 degree temps in big bulky space suits,)
Weight and payload
The Lunar Roving Vehicle had a weight of 463 lbs and was designed to hold a payload of an additional 1,080 lbs on the lunar surface. The frame was 10 feet long with a wheelbase of 7.5 feet. The maximum height was 3.75 feet. The frame was made of aluminum alloy 2219 tubing welded assemblies and consisted of a 3 part chassis which was hinged in the center so it could be folded up and hung in the Lunar Module quad 1 bay. It had two side-by-side foldable seats made of tubular aluminum with nylon webbing and aluminum floor panels. An armrest was mounted between the seats, and each seat had adjustable footrests and a velcro seatbelt. A large mesh dish antenna was mounted on a mast on the front center of the rover. The suspension consisted of a double horizontal wishbone with upper and lower torsion bars and a damper unit between the chassis and upper wishbone. Fully loaded the LRV had a ground clearance of 14 inches.
“Deployment of the LRV from the LM quad 1 by the astronauts was achieved with a system of pulleys and braked reels using ropes and cloth tapes. The rover was folded and stored in quad 1 with the underside of the chassis facing out. One astronaut would climb the egress ladder on the LM and release the rover, which would then be slowly tilted out by the second astronaut on the ground through the use of reels and tapes. As the rover was let down from the bay most of the deployment was automatic. The rear wheels folded out and locked in place and when they touched the ground the front of the rover could be unfolded, the wheels deployed, and the entire frame let down to the surface by pulleys.
The rover components locked into place upon opening. Cabling, pins and tripods would then be removed and the seats and footrests raised. After switching on all the electronics the vehicle was ready to back away from the LM.”

Ha Ha Ha Ha….Ha

CGI animators having a little break from their reality.

BEANS!
***
Arthur C. Clarke referred to Apollo 11 as a “Hole in History”.
Here is a study by analyst Jack White. He has studied this moon landing hoax more than anyone. Here, he puts it to the math test to show the impossibility of what NASA is asking us to believe. I visited several official NASA websites to find HOW MANY PHOTOS WERE TAKEN on the surface of the Moon. Amazingly, NASA AVOIDS THIS SUBJECT almost entirely. Two days of searching documents and text were fruitless. But Lunar Surface Journal, one of the sites, lists every photo with its file number. So I undertook to make an actual count of every photo taken by astronauts DURING EXTRA-VEHICULAR ACTIVITY (EVA), the time spent on the surface out of the LEM.
Here is my actual count of EVA photos of the six missions:
Apollo 11……….. 121 Apollo 12……….. 504 Apollo 14……….. 374 Apollo 15……….1021 Apollo 16……….1765 Apollo 17……….1986
So 12 astronauts while on the Moon’s surface took a TOTAL of 5771 exposures.
That seemed excessively large to me, considering that their TIME on the lunar surface was limited, and the astronauts had MANY OTHER TASKS OTHER THAN PHOTOGRAPHY. So I returned to the Lunar Surface Journal to find how much TIME was available to do all the scientific tasks AS WELL AS PHOTOGRAPHY. Unlike the number of photos, this information is readily available:
Apollo 11……..1 EVA …..2 hours, 31 minutes……(151 minutes) Apollo 12……..2 EVAs…..7 hours, 50 minutes……(470 minutes) Apollo 14……..2 EVAs…..9 hours, 25 minutes……(565 minutes) Apollo 15……..3 EVAs…18 hours, 30 minutes….(1110 minutes) Apollo 16……..3 EVAs…20 hours, 14 minutes….(1214 minutes) Apollo 17……..3 EVAs…22 hours, 04 minutes….(1324 minutes)
Total minutes on the Moon amounted to 4834 minutes. Total number of photographs taken was 5771 photos.
Hmmmmm. That amounts to 1.19 photos taken EVERY MINUTE of time on the Moon, REGARDLESS OF OTHER ACTIVITIES. (That requires the taking of ONE PHOTO EVERY 50 SECONDS!) Let’s look at those other activities to see how much time should be deducted from available photo time:
Apollo 11….Inspect LEM for damage, deploy flag, unpack and deploy radio and television equipment, operate the TV camera (360 degree pan), establish contact with Earth (including ceremonial talk with President Nixon), unpack and deploy numerous experiment packages, find/document/collect 47.7 pounds of lunar rock samples, walk to various locations, conclude experiments, return to LEM.
Apollo 12….Inspect LEM for damage, deploy flag, unpack and deploy radio and television equipment (spend time trying to fix faulty TV camera), establish contact with Earth, unpack and deploy numerous experiment packages, walk to various locations, inspect the unmanned Surveyor 3 which had landed on the Moon in April 1967 and retrieve Surveyor parts. Deploy ALSEP package. Find/document/collect 75.7 pounds of rocks, conclude experiments, return to LEM.
Apollo 14….Inspect LEM for damage, deploy flag, unpack and deploy radio and television equipment and establish contact with Earth, unpack and assemble hand cart to transport rocks, unpack and deploy numerous experiment packages, walk to various locations. Find/document/collect 94.4 pounds of rocks, conclude experiments, return to LEM.
Apollo 15….Inspect LEM for damage, deploy flag, unpack and deploy radio and television equipment and establish contact with Earth, unpack/assemble/equip and test the LRV electric-powered 4-wheel drive car and drive it 17 miles, unpack and deploy numerous experiment packages (double the scientific payload of first three missions). Find/document/collect 169 pounds of rocks, conclude experiments, return to LEM. (The LRV travels only 8 mph.)
Apollo 16….Inspect LEM for damage, deploy flag, unpack and deploy radio and television equipment and establish contact with Earth, unpack/assemble/equip and test the LRV electric-powered 4-wheel drive car and drive it 16 miles, unpack and deploy numerous experiment packages (double the scientific payload of first three missions, including new ultraviolet camera, operate the UV camera). Find/document/collect 208.3 pounds of rocks, conclude experiments, return to LEM. (The LRV travels only 8 mph.)
Apollo 17….Inspect LEM for damage, deploy flag, unpack and deploy radio and television equipment and establish contact with Earth, unpack/assemble/equip and test the LRV electric-powered 4-wheel drive car and drive it 30.5 miles, unpack and deploy numerous experiment packages. Find/document/collect 243.1 pounds of rocks, conclude experiments, return to LEM. (The LRV travels only 8 mph.)
Let’s arbitrarily calculate a MINIMUM time for these tasks and subtract from available photo time:
Apollo 11…subtract 2 hours (120 mins), leaving 031 mins for taking photos Apollo 12…subtract 4 hours (240 mins), leaving 230 mins for taking photos Apollo 14…subtract 3 hours (180 mins), leaving 385 mins for taking photos Apollo 15…subtract 6 hours (360 mins), leaving 750 mins for taking photos Apollo 16…subtract 6 hours (360 mins), leaving 854 mins for taking photos Apollo 17…subtract 8 hours (480 mins), leaving 844 mins for taking photos
So do the math:
Apollo 11…..121 photos in 031 minutes……..3.90 photos per minute Apollo 12…..504 photos in 230 minutes……..2.19 photos per minute Apollo 14…..374 photos in 385 minutes……..0.97 photos per minute Apollo 15…1021 photos in 750 minutes……..1.36 photos per minute Apollo 16…1765 photos in 854 minutes …….2.06 photos per minute Apollo 17…1986 photos in 844 minutes …….2.35 photos per minute
Or, to put it more simply:
Apollo 11……..one photo every 15 seconds Apollo 12……..one photo every 27 seconds Apollo 14……..one photo every 62 seconds Apollo 15……..one photo every 44 seconds Apollo 16……..one photo every 29 seconds Apollo 17……..one photo every 26 seconds
So you decide. Given all the facts, was it possible to take that many photos in so short a time?
Any professional photographer will tell you it cannot be done. Virtually every photo was a different scene or in a different place, requiring travel. As much as 30 miles travel was required to reach some of the photo sites. Extra care had to be taken shooting some stereo pairs and panoramas. Each picture was taken without a viewfinder, using manual camera settings, with no automatic metering, while wearing a bulky spacesuit and stiff clumsy gloves.
The agency wants the world to believe that 5771 photographs were taken in 4834 minutes!
Sources:
http://www.cluesforum.info/viewtopic.php?f=2&t=59&start=60
http://listverse.com/2012/12/28/10-reasons-the-moon-landings-could-be-a-hoax/
***
The Apollo astronauts used what was, at the time, a special transparency film produced by Eastman Kodak under a NASA contract. The photosensitive emulsions layers where placed on an ESTAR polyester film base, which had previously been used primarily for motion picture film. The melting point of Estar is 490° F, although some shrinkage and distortion can occur at around 200° F. Fortunately the film was never exposed to this kind of temperature. The cameras were protected inside a special case designed to keep them cool. The situation on the airless Moon is much different than in your oven, for instance. Without convection or conduction, the only method of heat transfer is radiation. Radiative heat can be effectively directed away from an object by wrapping it in a material with a reflective surface, usually simply a white material. The camera casings, as well as most of the astronauts’ clothing, were indeed white.
The black sky should be full of stars, yet none are visible in any of the Apollo photographs.
This claim is one I hear frequently, and is one of the easiest to refute. The answer is very simple: they are too faint. The Apollo photos are of brightly lit objects on the surface of the Moon, for which fast exposure settings were required. The fast exposures simply did not allow enough starlight into the camera to record an image on the film. For the same reason, images of Earth taken from orbit also lack stars. The stars are there; they just don’t appear in the pictures. The hoax advocates often argue that stars should be visible, and some of their claims are valid, however they fail to recognize the difference between “seeing” stars and “photographing” stars. The astronauts could have recorded star images in their photos by increasing exposures, but they were not there to take star pictures. The purpose of the photos was to record the astronauts’ activities on the surface of the Moon.
Da Bunkers blogroll
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Moon_landing_conspiracy_theories
 |
DID WE LAND ON THE MOON?A Debunking of the Moon Hoax Theory |
http://www.braeunig.us/space/hoax.htm
On February 15, 2001 the FOX television network aired a program titled Conspiracy Theory: Did We Land On The Moon? This program showed alleged evidence that NASA faked the moon landings. This hoax theory has been around for several years, but this is the first time it has been presented to such a wide audience. Since this Website, Rocket and Space Technology, is dedicated to the men and women who brought the moon landings to fruition, I feel the time is right for me to speak out on this topic.
This TV program capitalizes on America’s fixation with government conspiracies by sensationalizing the notion that NASA perpetrated a multi-billion dollar hoax on the world. In my opinion, the FOX network acted irresponsibly by airing this program. What they produced is a TV show filled with sloppy research, scientific inaccuracies and erroneous conclusions. To support such an absurd theory and to cast doubt in the minds of the American public is an insult to the courage of the astronauts and the brilliance of the engineers who worked to achieve mankind’s greatest technological feat. FOX is apparently only concerned with ratings while exhibiting total disregard for the integrity of America’s true heroes.
Some of the most prominent advocates of the hoax theory are Bill Kaysing, author of We Never Went To The Moon, Ralph Rene, author of NASA Mooned America, David Percy and Mary Bennett, co-authors of Dark Moon: Apollo and the Whistle Blowers and, more recently, Bart Sibrel, producer of A Funny Thing Happened On The Way To The Moon. These people, and other hoax advocates, usually point to alleged anomalies in the Apollo photo and video record as evidence of their claims. The FOX program featured many of these claims while providing very little refuting evidence or testimony. Below are my comments refuting both the evidence presented in the TV program and many other common hoax allegations. I invite you to draw your own conclusions, but I suspect you will find the facts speak for themselves.
The likelihood of success was calculated to be so small that it is inconceivable the moon landings could have actually taken place.
Bill Kaysing has claimed that the chance of a successful landing on the moon was calculated to be 0.0017% (1 in 60,000). The source of this information appears to be a report prepared by the Rocketdyne company in the late 1950s. This assessment was, of course, based on understanding and technology existing at the time of the report. As tremendous resources were poured into the problem over the next decade, the reliability studies improved dramatically.
During the mid-1960s the Apollo Support Department of the General Electric Company in Florida conducted extensive mission reliability studies for NASA. These studies were based on very elaborate reliability models of all of the systems. A reliability profile over the course of a mission was generated by computer simulation, and a large number of such simulations were carried out for different scenarios. Based on those studies, the probability of landing on the moon and returning safely to earth never dropped below 90%.
Every Apollo mission before number 11 was plagued by about 20,000 defects apiece. Yet, with the exception of Apollo 13, NASA claims there wasn’t one major technical problem on any of their Moon missions.
This is the claim of hoax advocate Ralph Rene. Although I am unfamiliar with the source of this information, Mr. Rene’s assertion is clear; the early missions had so many insurmountable problems that NASA decided to abandon the moon landings and fake it. Even if the data is accurate, there is a big difference between a “defect” and a “major technical problem”. None of the Apollo missions, with the exception of number 13, experienced a major technical problem that prohibited the crews from successfully completing their missions. Also, the early Apollo flights were test missions designed specifically to shake out bugs in the hardware and procedures. Finally, the moon landings were far from flawless. There were numerous technical problems but, thanks to the skill of the flight controllers, engineers and astronauts, the problems were either corrected or circumvented such that the crews were able to complete their missions with amazing success.
The poor video quality of the first moon landings was a deliberate ploy so nobody could properly examine it. ……………
…………


Leave a comment